The Critical Role of Refrigerant Management in Buildings
The Issue of Refrigerant Leakage
Refrigerants are indispensable for cooling but pose significant environmental risks when leaked, contributing notably to global warming. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), refrigerant leaks account for over 10% of greenhouse gas emissions. Implementing robust management practices to minimize these emissions is imperative.
Commissioning, Retro-Commissioning, and Decommissioning
The commissioning of new HVAC systems is crucial to ensure they operate at peak efficiency and remain leak-free. Retro-commissioning, on the other hand, serves to enhance the efficiency of existing systems. According to Energy Star, retro-commissioning can lead to an average reduction in energy consumption by about 15%, which also helps to minimize issues like refrigerant leaks by optimizing system performance. Similarly, proper decommissioning of HVAC systems is vital for preventing refrigerant leaks by ensuring efficient recovery and safe disposal of refrigerants.
Transitioning to Low GWP Refrigerants
Shifting to refrigerants with lower Global Warming Potential (GWP) is crucial for reducing environmental impacts. Innovations are fostering the adoption of alternatives like HFOs, ammonia, CO2, and hydrocarbons, which have significantly lower GWP than traditional HFCs. For instance, R-32 is increasingly used in residential HVAC systems due to its lower GWP compared to R-410A.
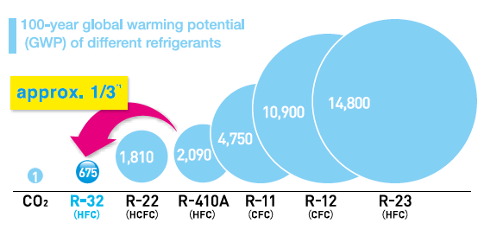
Regulatory and Industry Trends
The Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol mandates a global phasedown of high-GWP (Global Warming Potential) refrigerants, reflecting a significant regulatory push towards environmental sustainability in HVAC systems. In response to these regulations, recent industry trends have shown a marked shift towards more sustainable practices. This includes the advancement of leak detection technologies and the increasing adoption of natural refrigerants, which are less harmful to the environment compared to traditional high-GWP refrigerants. These trends highlight the industry’s commitment to reducing the climate impact of refrigerant gases and improving overall system efficiencies.
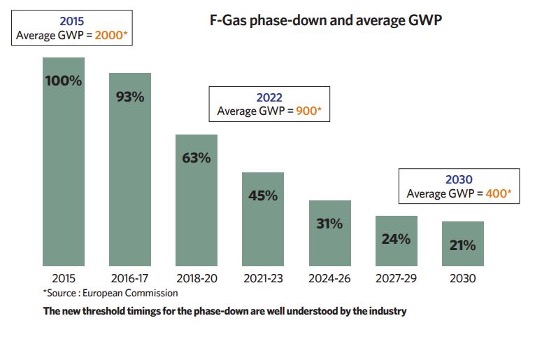
ESG Relevance of Refrigerant Management
Effective management of refrigerants is not only crucial for operational efficiency and environmental protection but also plays a significant role in an organization’s Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) strategy.
- Environmental Impact: Refrigerant management directly addresses the environmental concerns associated with harmful emissions. By preventing leaks and transitioning to low Global Warming Potential (GWP) refrigerants, organizations significantly reduce their ecological footprint. This is crucial, as refrigerants are potent greenhouse gases, and their management is critical in the fight against climate change.
- Social Responsibility: The aspect of refrigerant management that involves training and safeguarding the health of HVAC technicians and the general public also aligns with the social component of ESG. Proper training ensures that technicians handle refrigerants safely, reducing the risk of accidents and promoting workplace safety. Moreover, well-maintained and efficiently operating HVAC systems improve indoor air quality, which benefits the health and comfort of building occupants.
- Governance: Adhering to international and national regulations regarding refrigerant use, such as the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol, demonstrates strong governance. Organizations that proactively comply with these regulations are seen as more credible and reliable. Moreover, integrating refrigerant management into corporate policy reflects a commitment to legal compliance and ethical standards.
Challenges and Solutions
Managing refrigerants in HVAC systems presents significant challenges, including the detection of small leaks and retrofitting older systems to meet modern standards. To address these issues, the industry has turned to technological and educational solutions. Advanced leak detection systems have become crucial in identifying even the smallest leaks, which are critical to preventing significant environmental damage. Additionally, educational programs aimed at training technicians enhance the skills necessary to implement these sophisticated technologies effectively and ensure systems are both efficient and compliant with current regulations. These efforts not only solve immediate operational challenges but also contribute to long-term sustainability goals.
In Summary
Effective refrigerant management is essential for HVAC sustainability and wider decarbonization efforts. By adopting best practices and transitioning to low GWP refrigerants, the building sector can significantly reduce its climate impact. Continued regulatory support and industry innovation are key to sustainable refrigerant use.









